AI: Deep Learning
By now, you probably have the feeling why the terminology of neural networks and deep learning is used interchangeably. In fact, the neural network is “learning” the decision boundary based on how many datapoints are classified correctly and how many are classified incorrectly. This is done in two steps: the forward pass and the backpropagation step. In the forward pass, the neural network classifies all datapoints given its features. In the backpropagation step, we check how many datapoints are classified correctly. At one point in time, it is not possible to classify more datapoints correctly than we already have: this is our optimum.
But how do we build such a network? A neural network consists of nodes/neurons which are organised in layers. A neural network consists of one input layer, several hidden layers and one output layer. The amount of nodes chosen for the network depends on your dataset. For our coffee & tea dataset, we would define our network as follows:
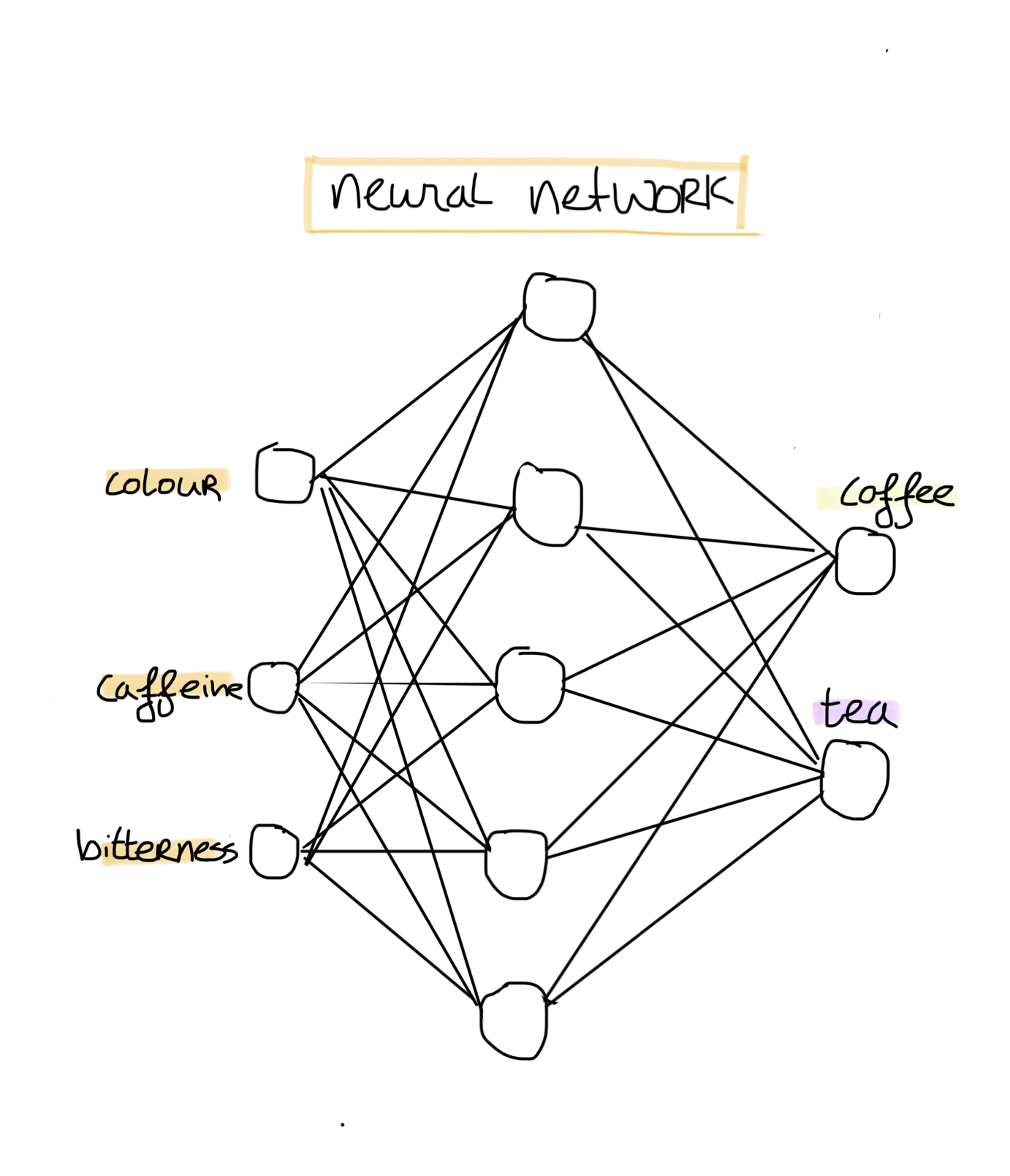
We have three input features, thus we choose three input neurons. Each input neuron is then used to model a feature. The hidden layer we can choose ourselves, depending on the chosen complexity of the model. As we want to classify whether our drink is coffee or tea, we have two output classes. Our output layer consists of two nodes. Our output neurons will model our output classes by using probabilities. Thus, the first output node would denote the probability that our drink is tea, and the second output node would denote the probability that our drink is coffee. Thus, the sum of our output neurons should be approximately 1.
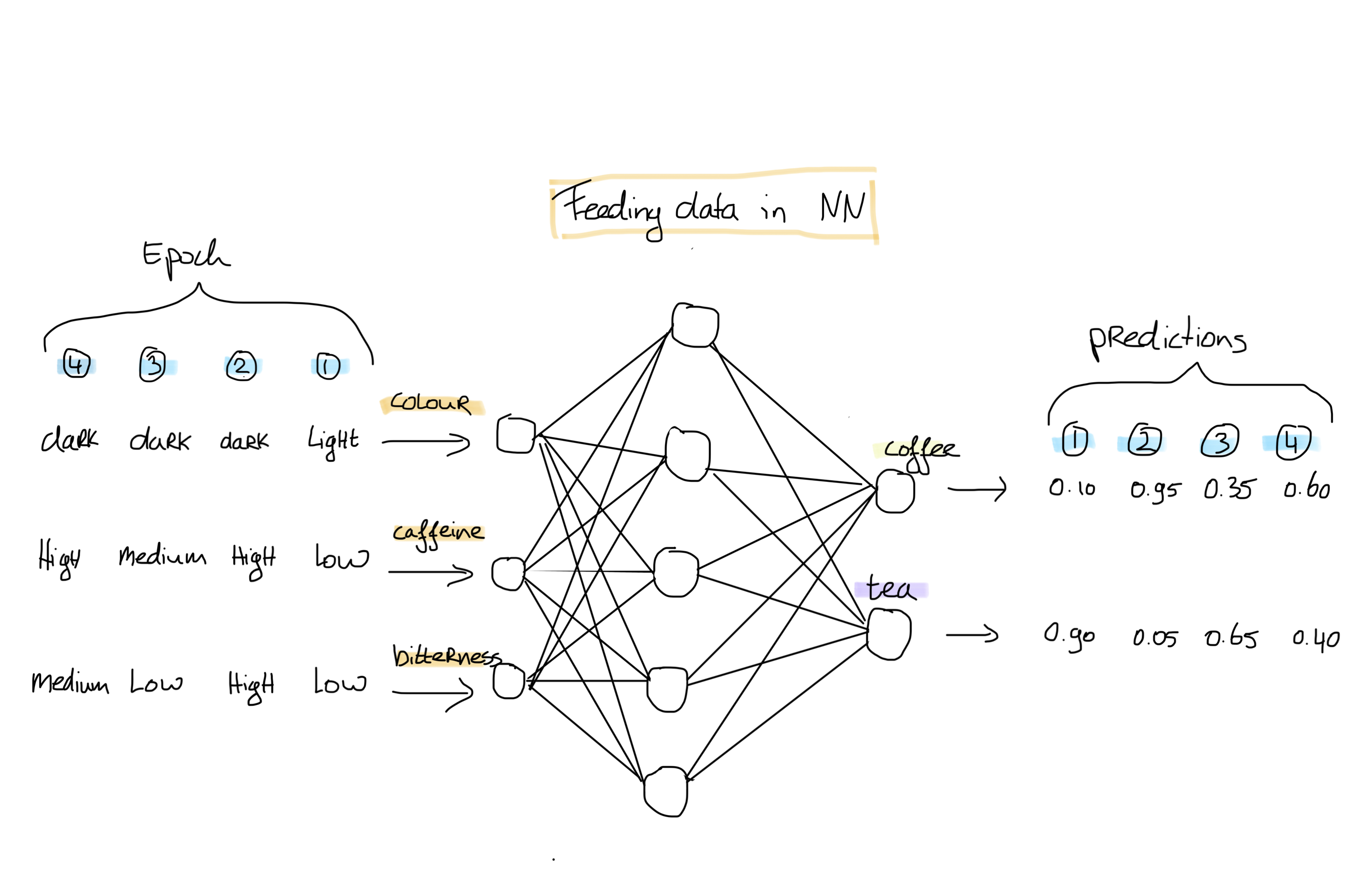
To train this network, we feed our first datapoint and label to our network. The network decides which of the features are more important to classify our drink, and which are less important. The weights between the nodes are updated accordingly. Based on the loss - i.e. how many datapoints are classified correctly - the network is adapted. Then, we put our second datapoint and label into the network. This sequence repeats until all datapoints are seen by the network.
It is also possible to show the dataset another time to the network, in case the network has not found an optimum yet. Epoch is the term used in the deep learning community to indicate how many times the whole dataset is passed through the network.
Keywords
- Backpropagation step - the step in the learning algorithm where mistakes are corrected by updating the weights
- Epoch - terminology for how often the dataset is passed through the network
- Forward pass - the step in the learning algorithm where datapoints are classified
- Loss - metric for the amount of mistakes made by the network. This is the function being minimalised
- Neuron- a basic computational unit within a neural network. Information flows through neurons and are multiplied by its weights depending on information importance
- Node - same as neuron
- Weights - the factor on how important a certain connection is between neurons. Used to give important features/nodes more power in the network and vice versa